
2ndgradeworksheets.net-Free worksheets and printables for teachers
Common Core State Standard 2.NBT.1
Number & Operations in Base Ten
Understand Place Value.
1. Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones. Understand the following as special cases:
a. 100 can be thought of as a bundle of ten tens — called a
“hundred.”
b. The numbers 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900 refer
to one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine hundreds (and
0 tens and 0 ones).
Common Core State Standards: 2.NBT.1
 Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Common Core State Standards:
2.NBT.1Numbers & Operations in Base Ten
Understand Place Value
Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones. Understand the following as special cases:
Students circle place value blocks to make a number.
 Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
Common Core State Standards:
2.NBT.1Numbers & Operations in Base Ten
Understand Place Value
Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones. Understand the following as special cases:
Students circle the place value blocks that represent the underlined digit.
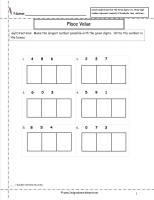 Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
Number Cards
Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
Number Cards
Common Core State Standards:
2.NBT.1Numbers & Operations in Base Ten
Understand Place Value
Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones. Understand the following as special cases:
Students make the biggest number possible with given digits.
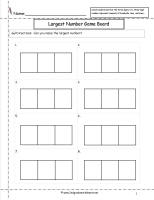 Biggest
Number Game
Biggest
Number Game
Common Core State Standards:
2.NBT.1Numbers & Operations in Base Ten
Understand Place Value
Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones. Understand the following as special cases:
Students make the biggest number possible with given digits.
 Place
Value Worksheet
2
3
4
5
Place
Value Worksheet
2
3
4
5
Common Core State Standards:
2.NBT.1Numbers & Operations in Base Ten
Understand Place Value
Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones. Understand the following as special cases:
Students write how many hundred, tens, or ones are shown.
 Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
Common Core State Standards:
2.NBT.1Numbers & Operations in Base Ten
Understand Place Value
Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones. Understand the following as special cases:
Students write the correct number shown by the digits and places.
 Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
Common Core State Standards:
2.NBT.1Numbers & Operations in Base Ten
Understand Place Value
Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones. Understand the following as special cases:
Students trade ones and tens.
 Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
Place
Value Worksheet 1
2
Common Core State Standards:
2.NBT.1Numbers & Operations in Base Ten
Understand Place Value
Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones; e.g., 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones. Understand the following as special cases:
Students write the value of the underlined digits.